Knowledge is the foundation of progress, shaping the way we grow, analyze, and innovate. In today’s digital age,the ability to efficiently find, understand, and apply knowledge is more crucial than ever. It fuelspersonal growth, professional success, and critical thinking.
But here’s the problem: the internet is overloaded with information, making it increasingly difficult to distinguish facts from misinformation. This is where Wiseone, your AI-powered research assistant, comes in, to help you unlock trusted, relevant, and actionable knowledge in seconds.
Why knowledge is more important than ever ?
Knowledge isn’t just about memorizing facts; it’s about understanding, analyzing, and applying insights to make smarter decisions. There are two key types of knowledge:
- Propositional knowledge (knowing that): Understanding facts, theories, and concepts (e.g., “The Earth orbits the Sun”).
- Practical knowledge (knowing how): The ability to apply what you know in real-world situations (e.g., “How to analyze research papers efficiently”).
Philosophers like Gilbert Ryle have debated this distinction, emphasizing that knowing how to do something is different from just knowing about it.
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s not just about accessing information, it’s about getting precise, contextual, and reliable insights quickly.
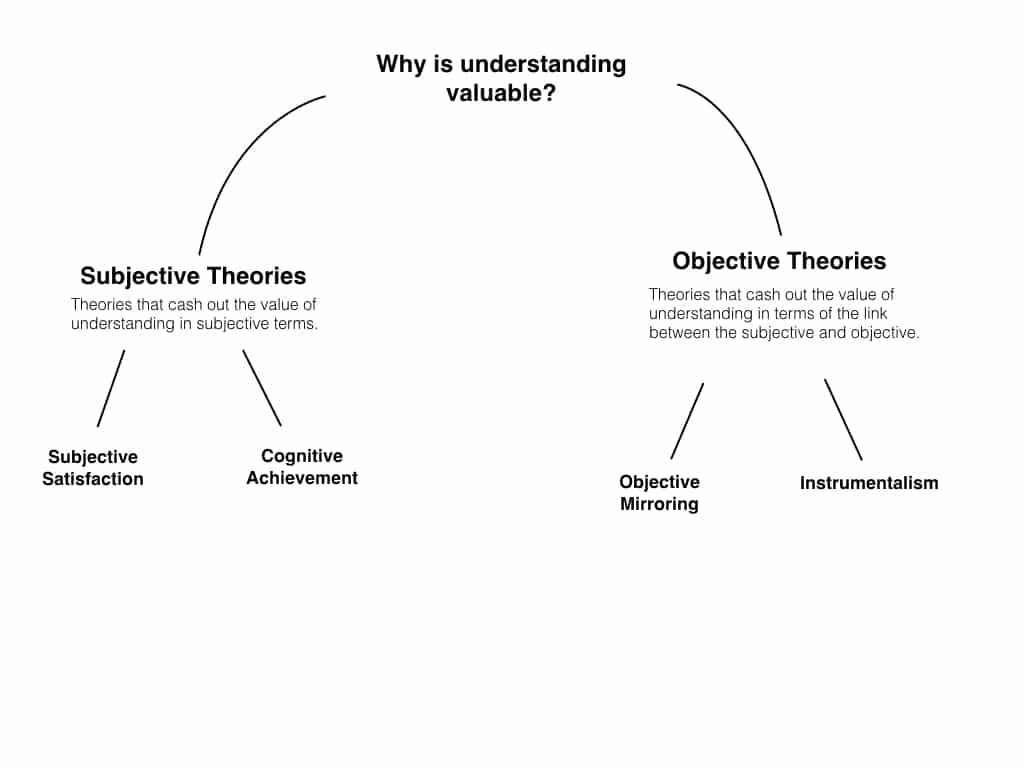
Ryle argued that knowledge relates to a proposition involving the apprehension of truths or facts. People typically refer to this type of knowledge when they discuss facts, such as knowing that the Earth orbits the Sun.
On the other hand, practical knowledge, or knowledge-how, relates to the ability to perform specific tasks. Examples include knowing how to ride a bicycle, swim, or play an instrument. This type of knowledge is typically implicit, demonstrated through action rather than articulated in factual statements. It involves skills and competencies acquired through practice and experience rather than theoretical understanding.
Economic and societal implications of knowledge
In the economic context, Friedrich Hayek emphasized the importance of knowledge in society, particularly how it helps efficiently coordinate and utilize resources. Hayek’s insights suggest that knowledge is not just an individual asset but a dispersed entity that plays a critical role in societal organization and economic systems.
Personal development and knowledge
Knowledge contributes significantly to personal development. It helps individuals improve self-awareness, build skills, increase self-esteem, and achieve personal and professional goals. This form of development is viewed as a broader aspect of one’s life, influencing not just career paths but also personal growth and well-being.
How to enhance knowledge about everything
Set clear goals
Setting clear learning goals guides the journey to gaining knowledge. Without defined goals, acquiring knowledge can lack direction and purpose. Goals provide a clear focus, helping you prioritize what you want to learn and why. They structure your learning efforts and can be tailored to your interests, whether you’re enhancing your knowledge base, acquiring new skills, or staying updated on specific topics. By articulating your objectives, you establish a roadmap that propels you forward, motivates your learning endeavors, and increases your commitment to the process.
For instance, set a goal to learn a new programming language within a specific timeframe or deepen your understanding of global politics by reading several weekly articles.
Another example could be improving your communication skills by taking a public speaking course. Establishing concrete, measurable, and achievable goals creates a tangible framework for your learning endeavors and enables you to track your progress.
Wiseone: your AI-powered knowledge assistant
Traditional search engines give you a long list of links, but Wiseone does the heavy lifting for you:
- Summarizes complex topics in seconds
- Cross-checks multiple sources to verify accuracy
- Filters out misinformation to provide only trusted insights
- Allows you to interact with articles, PDFs, and research papers seamlessly
💡 Imagine researching a topic and getting a clear, fact-checked summary in seconds—no more endless scrolling.
Transform the way you research, learn, and stay informed
- Students & researchers: Save time on academic research with instant summaries & source verification
- Professionals & analysts: Stay ahead in your industry by quickly digesting trends and insights
- Curious minds: Cut through information overload and get fact-based, structured knowledge instantly
Don’t just read, understand. Don’t just search, discover.
Taking advantage of dedicated tools
As AI continues gaining popularity, leveraging AI tools becomes crucial for enhancing knowledge and learning new skills.
Among these tools lies Wiseone, an innovative AI tool that transforms how we read and search for information online.
👉 Try Wiseone now and revolutionize the way you access knowledge!
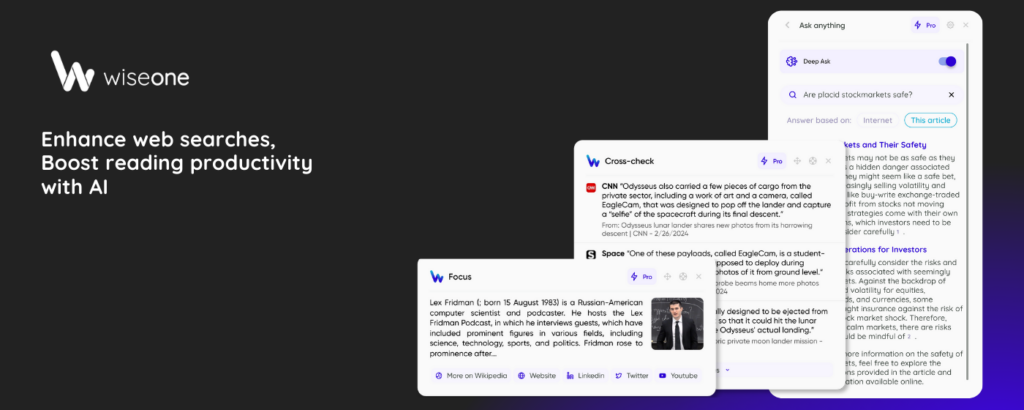
Wiseone enhances knowledge by providing extensive features designed with the best LLMs available today.
Here’s how it happens:
- Direct query answers: You can type queries on search engines and receive comprehensive answers directly. The answers provided include references to the sources, allowing easy access for further exploration.
- Summarization: Wiseone’s “Summarize” feature allows you to understand the main points of an article or a PDF document efficiently without the need to read the entire piece by generating thorough summaries with key takeaways.
- Cross-referencing: With cross-checking, Wiseone simplifies fact-checking and quick access to credible information by generating curated lists of news articles reporting on the same topic.
- Effortless information access: The “Explore” feature provides quick access to related topics, enabling users to gain deeper insights into any subject matter.
- Explaining complex words: Wiseone ensures a thorough understanding of words to comprehend 100% of the content, mainly complex terms and concepts, with the feature “Focus.”
Cultivate curiosity
Curiosity is a strong desire to know or learn, having an interest in a person, thing, or experience that leads to inquiring. Here’s how to cultivate it:
-
- Identify motivations: The first step in enhancing curiosity is to know and understand what motivates you. Recognizing what intrigues an individual can help guide your curious impulses more constructively.
- Sense of wonder: This involves seeing things as if for the first time, even ordinary or familiar situations. By adopting a mentality that appreciates everyday life, you can maintain a continual interest in exploring and understanding your environment.
- Ask more
- Engage with Diverse Experiences
To broaden your horizons and enhance your curiosity, seek new and diverse experiences. This could involve reading broadly, traveling, attending workshops, or simply conversing with people whose views and backgrounds differ from yours. Each new experience is an opportunity to learn and become curious about different aspects of the world.
Use diverse knowledge channels
Diversity in learning channels refers to methods, platforms, and tools through which education and training can be delivered to students or employees. These channels can include traditional classroom settings, online platforms, blended learning environments, and multichannel multimodal learning (MML) approaches.
Formal education provides a structured framework for learning because it equips students with knowledge, critical thinking skills, and academic credentials crucial for personal and professional advancement.
However, nowadays, modern learning resources have changed by providing access to information and empowering self-learners.
Now, multiple online platforms offer various courses in different subjects, allowing people to learn at their own pace, anytime, anywhere.
-
-
- Another form of learning that has also become popular is podcasts, which offer:
- Immersive learning experiences.
- Engaging discussions.
- Interviews with diverse and exciting people.
- Expert insights.
-
Educational apps have also become known for leveraging technology and AI to provide interactive learning experiences, challenges, and personalized feedback, making knowledge accessible, easy to have, and enjoyable.
Embrace effective learning strategies
Adopting effective learning strategies is also essential to enhancing knowledge and learning new information. Active learning techniques like active recall, spaced repetition, and concept mapping improve retention and understanding.
-
-
- Active recall involves retrieving information from memory rather than passively reviewing material, reinforcing neural connections, and strengthening recall.
- On the other hand, spaced repetition involves revisiting information at increasing intervals over time, optimizing long-term retention by leveraging the spacing effect.
- A concept map visually displays the relationships between different concepts, ideas, and pieces of information. Concept maps are hierarchical, with one main idea or focus question and several subtopics, key concepts, and related ideas.
-
Incorporating these active learning strategies into our study routines allows us to maximize our cognitive efficiency and accelerate learning.
Moreover, understanding and tailoring learning styles to individual preferences can significantly enhance learning outcomes.
Learning styles
Auditory learning style
Auditory learners learn best through their sense of hearing. This means they remember and understand new concepts better when they are explained out loud—even if they’re speaking themselves. They can even better retain knowledge when new ideas are paired with nonverbal sounds such as music, drum beats, or clapping.
Visual learning style
Visual learners learn more when their sense of sight is engaged. They quickly show an affinity for books and reading, starting with picture books and promptly moving on to books with text. Bright colors and clear diagrams engage them, and they can learn from videos, demonstrations, and classroom handouts. Of the three different learning styles, visual learning most closely conforms to traditional classroom teaching methods. Visual learners can glean information from reading assignments, from taking and reviewing handwritten notes, and from the flip charts, diagrams, and other visual aids that many teachers use.
Kinesthetic learning style
The most physical of all learning styles, kinesthetic learners absorb information best through touch, movement, and motion. The word kinesthetic refers to our ability to sense body position and movement. This means that to understand something, they need to touch, feel, and move it around.
Individuals can optimize their knowledge and study approaches to suit their unique strengths and preferences by identifying a preferred learning style and dedicating techniques that align with it.
Micro-learning
Micro-learning is based on scientific knowledge. It uses spaced retrieval, a well-proven method of boosting retention. It is achieved by breaking down learning topics into smaller bits that can be easily understood and repeating them with adequate spacing between lessons.
This learning technique gives learners retentive memory capabilities, making micro-learning suitable for acquiring technical skills.
Some micro-learning content examples include:
-
-
- Text (phrases, short paragraphs)
- Videos (of the short variety)
- Audio (short snippets of speech or music)
- Tests and quizzes
- Games (e.g., simple single-screen challenges)
- Images (photos, illustrations)
-
Enhance knowledge from experience and real-life situations
Enhancing knowledge from experience and real-life situations is like refining raw material into a masterpiece.
While formal education provides the base and foundation, applying knowledge in real-world scenarios enriches our understanding.
Whether through triumphs or challenges, every experience offers valuable lessons that cannot be learned from books alone.
Real-life situations challenge us to think critically, problem-solve creatively, and adapt to diverse circumstances, improving our skills and deepening our insights. This can happen at work, traveling to a new country, or overcoming personal issues.
By actively seeking out new experiences and embracing the lessons they offer, we open ourselves up to a world of continuous learning and growth.
Through real-life experiences, knowledge transforms into wisdom, guiding us toward self-discovery and mastery.
FAQ
What is the value of knowledge?
The value of knowledge is multifaceted, encompassing philosophical debates, practical applications, and personal growth.
Whether it enhances cognitive functions, enriches personal lives, or contributes to societal progress, knowledge remains important in human development and civilization.
How can we enhance knowledge about everything?
We can enhance knowledge by setting clear goals, taking advantage of dedicated tools, cultivating curiosity, using diverse knowledge channels, embracing effective learning solutions, micro-learning, and gaining insights from real-life experiences.
What are the different learning styles?
Auditory learning style: Auditory learners learn best through their sense of hearing. They remember and understand new concepts better when explained aloud. They can retain knowledge even better when new ideas are paired with nonverbal sounds such as music, drum beats, or clapping.
Visual learning style: Visual learners engage best when their sense of sight is activated. They are drawn to books, bright colors, and diagrams. They learn effectively from videos, demonstrations, and classroom handouts.
Kinesthetic learning style: Kinesthetic learners absorb information best through touch, movement, and motion. They need to physically interact with an object, move around, or engage in hands-on activities to fully understand concepts.
What does micro-learning include?
Some micro-learning content examples include:
- Images (photos, illustrations)
- Text (phrases, short paragraphs)
- Videos (short clips)
- Audio (brief speech or music snippets)
- Tests and quizzes
- Games (e.g., single-screen challenges)
What is Wiseone ?
Wiseone is an innovative AI tool that transforms how we read and search for information online.
Wiseone enhances knowledge by providing extensive features designed with the best LLMs available today.

